Documentation | InterfaceKit | AffineTransform
SYNOPSIS
Perl
use HaikuR1::AffineTransform; my $transform = HaikuR1::AffineTransform->new($sx, $shy, $shx, $sy, $tx, $ty); my $result = $transform->Apply($x, $y);
Python
from HaikuR1.InterfaceKit import AffineTransform transform = AffineTransform(sx, shy, shx, sy, tx, ty) result = transform.Apply(x, y)
DESCRIPTION
Exposes the BAffineTransform object.
For more information on AffineTransform, see the Haiku Book class description. (Which at the time of writing, does not yet exist, but hopefully will soon.
Until then, you can read the Wikipedia article) about affine transformations.
This object supports four kinds of simple transformations: scaling, shearing, rotation, and translation. It also supports complex transformations consisting of multiple simple transformations.
For example, consider a square:
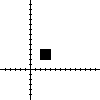
<!-- ASCII
. .
. .
+
-->
Translation
Translation simply moves the square.
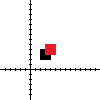
<!-- ASCII
. .
. .
+
-->
Rotation
Rotation rotates the square around some point (by default, the origin). In this case, the rotation is 45 degrees.
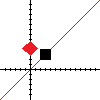
<!-- ASCII . . . . + -->
Scaling
Scaling makes the square larger or smaller. Notice that the distance from the origin is also scaled. (The use of the origin is by default; another point can be specified.) The example below scales uniformly in both directions, but it is also possible to specify different scales for each direction.
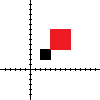
<!-- ASCII
. .
. .
+
-->
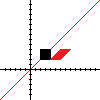
Shearing
Shearing "leans" the square. The example below leans the square 45 degrees to the right, and does not lean it vertically. Note that once again, the "lean" is relative to a point, by default the origin.
(Rotation is technically a shearing in two complementary directions. The rotation above could have been implemented by shearing 45 degrees to the left and 45 degrees up.)
<!-- ASCII
. .
. .
+
-->
Angles
Although we used degrees above, the methods below actually take angles in radians. For reference:
- 90° = π/2; radians;
- 180° = π radians;
- 270° = 3π/2 radians;
- 360° = 2π radians;
- x° = (x/180) * π radians;
PROPERTIES
sx, sy
Scaling factors along the given axis.
shx, shy
Shearing factor along the given axis. (These are the tangents of the desired angles, not the angles themselves.)
tx, ty
Translation along the given axis.
METHODS
Constructor
Creates an AffineTransform.
Perl
HaikuR1::AffineTransform->new($sx, $shy, $shx, $sy, $tx, $ty); HaikuR1::AffineTransform->new($copy_from); HaikuR1::AffineTransform->new();
Python
AffineTransform(sx, shy, shx, sy, tx, ty) AffineTransform(copy_from) AffineTransform()
sx,sy
Floating point numbers, the scaling factors.
shx,shy
Floating point numbers, the shearing factors.
tx,ty
Floating point numbers, the translation factors.
copy_fromAn AffineTransform to copy.
Notes:
- Pay attention to the order of the arguments.
- The version with no arguments creates an identity transformation
- See the class methods below for a more intuitive way to create transformations.
copy
Copies the contents of another object into this object.
Perl
$affinetransform->copy($copy_from);
Python
affinetransform.copy(copy_from)
copy_fromAn AffineTransform to copy.
Apply
ApplyInverse
Applies the transform (or its inverse) to the given point or points.
Perl
$affinetransform->Apply($x, $y); $affinetransform->Apply($point); $affinetransform->Apply($points); $affinetransform->ApplyInverse($x, $y); $affinetransform->ApplyInverse($point); $affinetransform->ApplyInverse($points);
Python
affinetransform.Apply(x, y) affinetransform.Apply(point) affinetransform.Apply(points) affinetransform.ApplyInverse(x, y) affinetransform.ApplyInverse(point) affinetransform.ApplyInverse(points)
x,y
Floating point numbers, a single point.
point
A single Point object.
points
A native list of Points.
Determinant
InverseDeterminant
Returns the determinant (or the inverse of the determinant) for the transformation matrix.
Perl
$affinetransform->Determinant(); $affinetransform->InverseDeterminant();
Python
affinetransform.Determinant() affinetransform.InverseDeterminant()
Factors
GetTranslation
Rotation
Scale
GetScale
GetScaleAbs
GetAffineParameters
Returns the translation factors, angle of rotation, scale, or all factors.
Scale returns the mean scaling factor, GetScale returns the two scaling
factors, and GetScaleAbs returns the absolute values of the scaling
factors. (This is not the absolute value of each individual scaling factor,
but the distance of the scales from the origin.)
GetAffineParameters returns 7 values.
- x-translation: how much the x value would be changed by the translation factors
- y-translation: how much the y value would be changed by the translation factors
- rotation: the angle of rotation
- x-scaling: the effect of the scaling factors on the x-value
- y-scaling: the effect of the scaling factors on the y-value
- x-shearing: the effect of the shearing factors on the y-value
- y-shearing: the effect of the shearing factors on the x-value
(Yes, the shearing parameters look backward to me, too, but that's how they're coded in the underlying C++ method.)
Perl
$affinetransform->GetTranslation(); $affinetransform->Rotation(); $affinetransform->Scale(); $affinetransform->GetScale(); $affinetransform->GetScaleAbs(); $affinetransform->GetAffineParameters();
Python
affinetransform.GetTranslation() affinetransform.Rotation() affinetransform.Scale() affinetransform.GetScale() affinetransform.GetScaleAbs() affinetransform.GetAffineParameters()
Flips
FlipX
FlipY
Alters the transform so that the resulting point would be flipped with respect to the given axis.
Flips the x coordinate of the result; returns the AffineTransform as a convenience.
Perl
$affinetransform->FlipX(); $affinetransform->FlipY();
Python
affinetransform.FlipX() affinetransform.FlipY()
Invert
Inverts the AffineTransform; returns the AffineTransform as a convenience.
(A transform multiplied by its inverse is the identity transform.)
Perl
$affinetransform->Invert();
Python
affinetransform.Invert()
Multiply
PreMultiply
Multiplies this transform by another (or its inverse).
Multiplication of transforms is not commutative; the order of the transforms
makes a difference. Multiply multiplies this transform by the other
transform; PreMultiply multiplies the other transform by this transform.
Perl
$affinetransform->Multiply($other); $affinetransform->MultiplyInverse($other); $affinetransform->PreMultiply($other); $affinetransform->PreMultiplyInverse($other);
Python
affinetransform.Multiply(other) affinetransform.MultiplyInverse(other) affinetransform.PreMultiply(other) affinetransform.PreMultiplyInverse(other)
other
An AffineTransform, the AffineTransform to multiply by.
Reset
Restores the AffineTransform to its default values (that is, the identity transformation); returns the AffineTransform as a convenience.
Perl
$affinetransform->Reset();
Python
affinetransform.Reset()
RotateBy
RotateByCopy
PreRotateBy
Applies a rotation to this AffineTransform; basically, this consists of
multiplying this transform by a transform consisting of a simple rotation.
(PreRotateBy multiples the simple translation by this transform.)
RotateByCopy leaves this transform alone and performs the operation on a
copy. The others perform the operation on this transform and return a copy of
the result.
Perl
$affinetransform->RotateBy($angle); $affinetransform->RotateBy($center, $angle); $affinetransform->RotateByCopy($angle); $affinetransform->RotateByCopy($center, $angle); $affinetransform->PreRotateBy($angle);
Python
affinetransform.RotateBy(angle) affinetransform.RotateBy(center, angle) affinetransform.RotateByCopy(angle) affinetransform.RotateByCopy(center, angle) affinetransform.PreRotateBy(angle)
center
A Point, the center of rotation (defaults to origin).
angle
A floating point number, the angle of rotation (in radians).
SetScale
Replaces the existing scaling factor; returns this AffineTransform as a convenience.
Perl
$affinetransform->SetScale($x, $y); $affinetransform->SetUniformScale($scale);
Python
affinetransform.SetScale(x, y) affinetransform.SetUniformScale(scale)
x,y
Floating point numbers, the scaling factors.
scale
A floating point number, a uniform scaling factor.
ScaleBy
ScaleByCopy
PreScaleBy
Applies a scaling to this AffineTransform; basically, this consists of
multiplying this transform by a transform consisting of a simple scaling.
(PreScaleBy multiples the simple translation by this transform.)
ScaleByCopy leaves this transform alone and performs the operation on a
copy. The others perform the operation on this transform and return a copy of
the result.
Applies a uniform scaling factor to this AffineTransform using the current translation as the center; returns this AffineTransform as a convenience.
Perl
$affinetransform->ScaleBy($x, $y); $affinetransform->ScaleBy($center, $x, $y); $affinetransform->ScaleBy($scale); $affinetransform->ScaleBy($center, $scale); $affinetransform->ScaleByCopy($x, $y); $affinetransform->ScaleByCopy($center, $x, $y); $affinetransform->ScaleByCopy($scale); $affinetransform->ScaleByCopy($center, $scale); $affinetransform->PreScaleBy($x, $y);
Python
affinetransform.ScaleBy(x, y) affinetransform.ScaleBy(center, x, y) affinetransform.ScaleBy(scale) affinetransform.ScaleBy(center, scale) affinetransform.ScaleByCopy(x, y) affinetransform.ScaleByCopy(center, x, y) affinetransform.ScaleByCopy(scale) affinetransform.ScaleByCopy(center, scale) affinetransform.PreScaleBy(x, y)
center
A Point, the center of scaling (defaults to origin).
x,y
Floating point numbers, the scaling factors.
scale
A floating point number, a uniform scaling factor; or a Point, distinct horizontal and vertical scaling factors.
ShearBy
ShearByCopy
Applies scaling factors to this AffineTransform using the current translation as the center; returns this AffineTransform as a convenience.
Perl
$affinetransform->ShearBy($x, $y); $affinetransform->ShearBy($center, $x, $y); $affinetransform->ShearBy($shear); $affinetransform->ShearBy($center, $shear); $affinetransform->ShearByCopy($x, $y); $affinetransform->ShearByCopy($center, $x, $y); $affinetransform->ShearByCopy($shear); $affinetransform->ShearByCopy($center, $shear);
Python
affinetransform.ShearBy(x, y) affinetransform.ShearBy(center, x, y) affinetransform.ShearBy(shear) affinetransform.ShearBy(center, shear) affinetransform.ShearByCopy(x, y) affinetransform.ShearByCopy(center, x, y) affinetransform.ShearByCopy(shear) affinetransform.ShearByCopy(center, shear)
center
A Point, the center of shearing (defaults to origin).
x,y
Floating point numbers, the shearing angles.
shear
The shearing angles as a Point object.
Tests
IsValid
IsIdentity
IsDilation
IsEqual
Returns true if the given test passes. Since many real numbers cannot be represented by a floating point number, small errors may creep in during multiplication of factors, so a tolerance is used when making these comparisons.
A transform is valid if both of its scaling factors are non-zero (within the given tolerance); this is because a zero scaling factor would map all points to zero.
The identity transform is one that does not change the points to which it is
applied; that is, the scaling factors are both 1 and the other factors are
zero (within the given tolerance).
A transform is a dilation if both of its shearing angles are zero (or a multiple of 360° == 2π radians, within the given tolerance); that is, a dilation does not change the angles of a shape it is applied to, because it only scales or translates the points.
Two transforms are equal if all of their factors are equal (within the given tolerance).
Perl
$affinetransform->IsValid($epsilon); $affinetransform->IsIdentity($epsilon); $affinetransform->IsDilation($epsilon); $affinetransform->IsEqual($other, $epsilon);
Python
affinetransform.IsValid(epsilon) affinetransform.IsIdentity(epsilon) affinetransform.IsDilation(epsilon) affinetransform.IsEqual(other, epsilon)
TranslateBy
TranslateByCopy
PreTranslateBy
Applies a translation to this AffineTransform; basically, this consists of
multiplying this transform by a transform consisting of a simple translation.
(PreTranslateBy multiples the simple translation by this transform.)
TranslateByCopy leaves this transform alone and performs the operation on a
copy. The others perform the operation on this transform and return a copy of
the result.
Perl
$affinetransform->TranslateBy($x, $y); $affinetransform->TranslateBy($delta); $affinetransform->TranslateByCopy($x, $y); $affinetransform->TranslateByCopy($delta); $affinetransform->PreTranslateBy($x, $y);
Python
affinetransform.TranslateBy(x, y) affinetransform.TranslateBy(delta) affinetransform.TranslateByCopy(x, y) affinetransform.TranslateByCopy(delta) affinetransform.PreTranslateBy(x, y)
x,y
Floating point numbers, the translation factors.
delta
The translation factors as a Point object.
other
An AffineTransform to compare against.
epsilon
A floating point number, the tolerance to use when comparing; defaults to
kDefaultEpsilon.
CLASS METHODS
Shortcuts
AffineTranslation
AffineRotation
AffineScaling
AffineShearing
Shortcut methods that create an AffineTransform object for the given transformation.
Perl
HaikuR1::AffineTransform->AffineTranslation($x, $y); HaikuR1::AffineTransform->AffineRotation($angle); HaikuR1::AffineTransform->AffineScaling($x, $y); HaikuR1::AffineTransform->AffineScaling($scale); HaikuR1::AffineTransform->AffineShearing($x, $y);
Python
AffineTransform.AffineTranslation(x, y) AffineTransform.AffineRotation(angle) AffineTransform.AffineScaling(x, y) AffineTransform.AffineScaling(scale) AffineTransform.AffineShearing(x, y)
x,y
Floating point numbers, the translation or scaling factors, or shearing angles.
angle
A floating point number, the angle of rotation.
scale
A floating point number, a uniform scaling factor.
FLATTENABLE INTERFACE
AffineTransform inherits the methods and hooks of Flattenable.
The following differ from the Flattenable versions:
IsFixedSize
Always return true.
TypeCode
Returns B_AFFINE_TRANSFORM_TYPE.
AllowsTypeCode
Checks against B_AFFINE_TRANSFORM_TYPE.
OPERATORS
==
Returns true if the transformations are equal within the default tolerance.
!=
Returns true if the transformations are not equal within the default
tolerance.
*
Multiplies the first transformation by the second (remember that order matters!) and returns the result.
/
Multiplies the first transformation by the inverse of the second and returns the result.
*=
Multiplies in place the first transformation by the second.
/=
Multiplies in place the first transformation by the inverse of the second.
~
Returns the inverse of the transformation.
CONSTANTS
kDefaultEpsilon
The default tolerance for comparison operations; at the time of writing, this is
0.000 000 000 000 01.B_AFFINE_IDENTITY_TRANSFORM
The identity transformation.